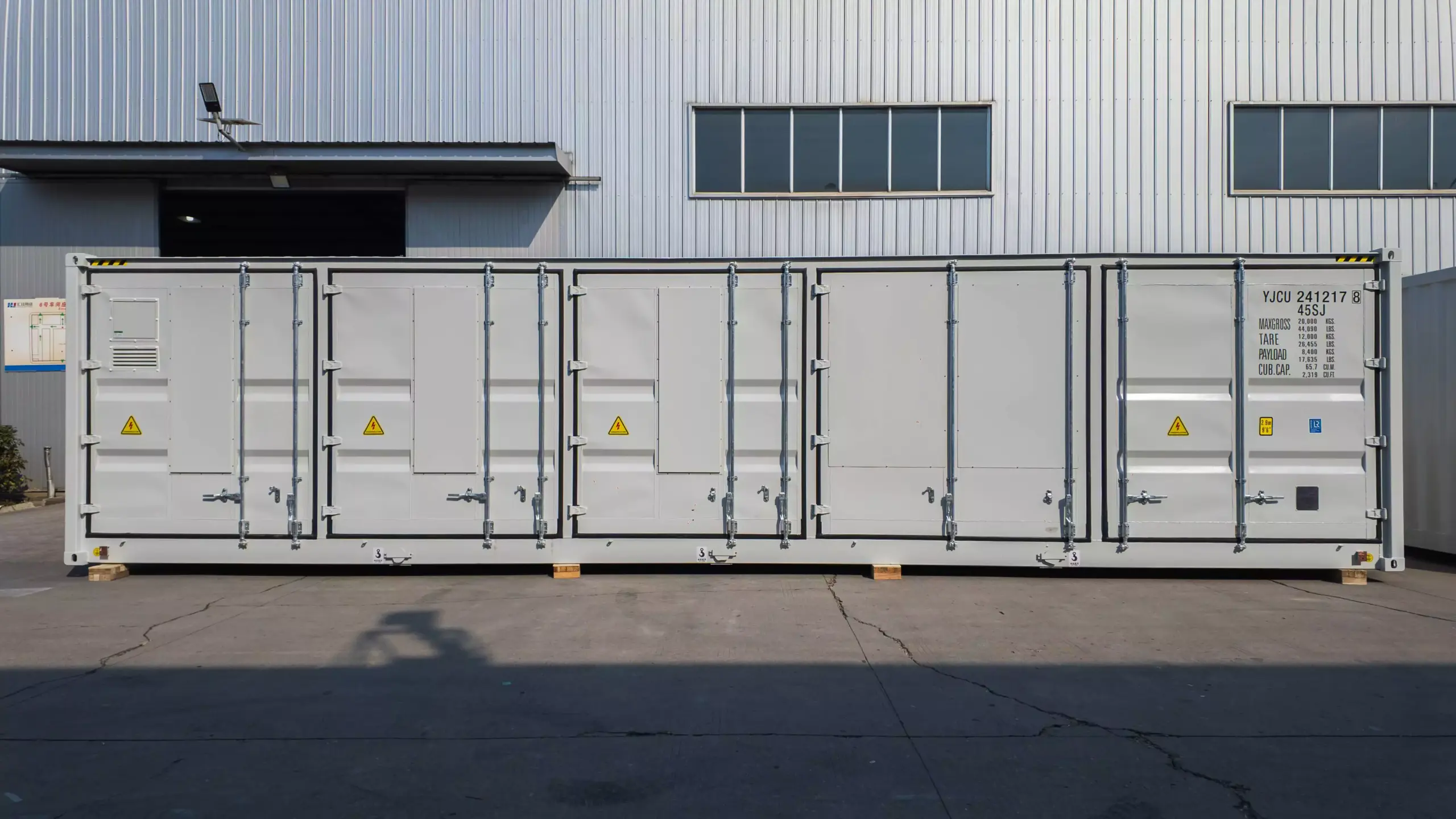

2025-03-06 MORE+
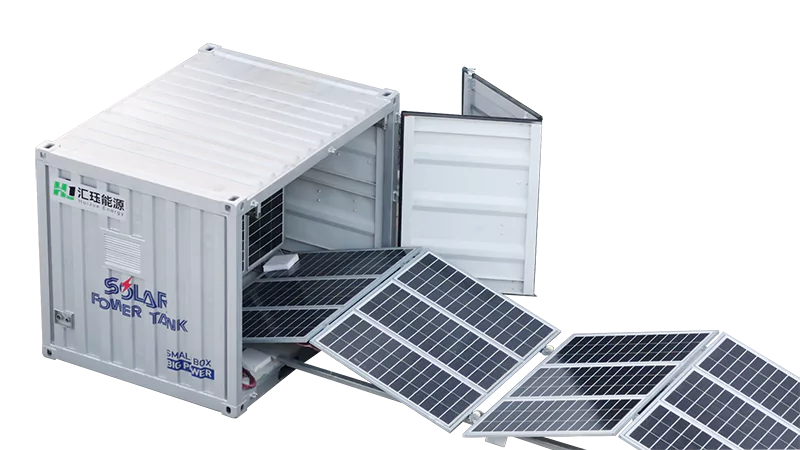

2025-02-19 MORE+
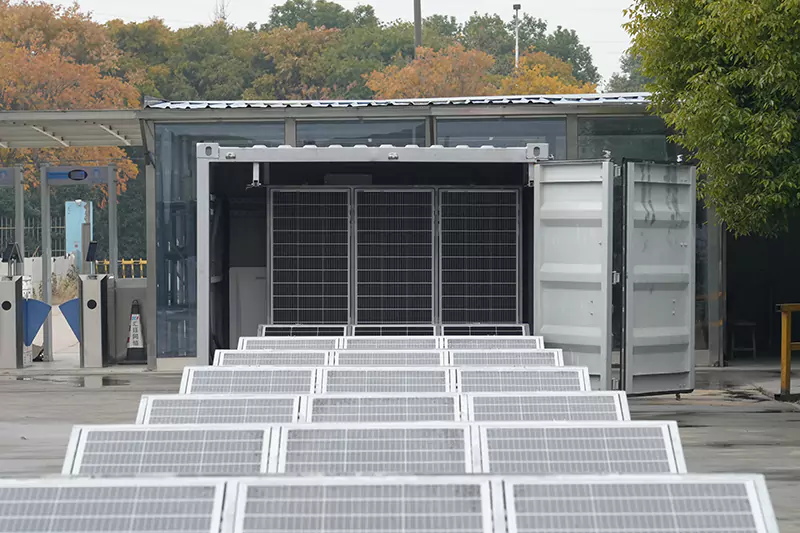

2025-02-19 MORE+
2024-12-26 MORE+

2024-12-26 MORE+

2024-12-26 MORE+

2024-12-26 MORE+

2024-12-26 MORE+
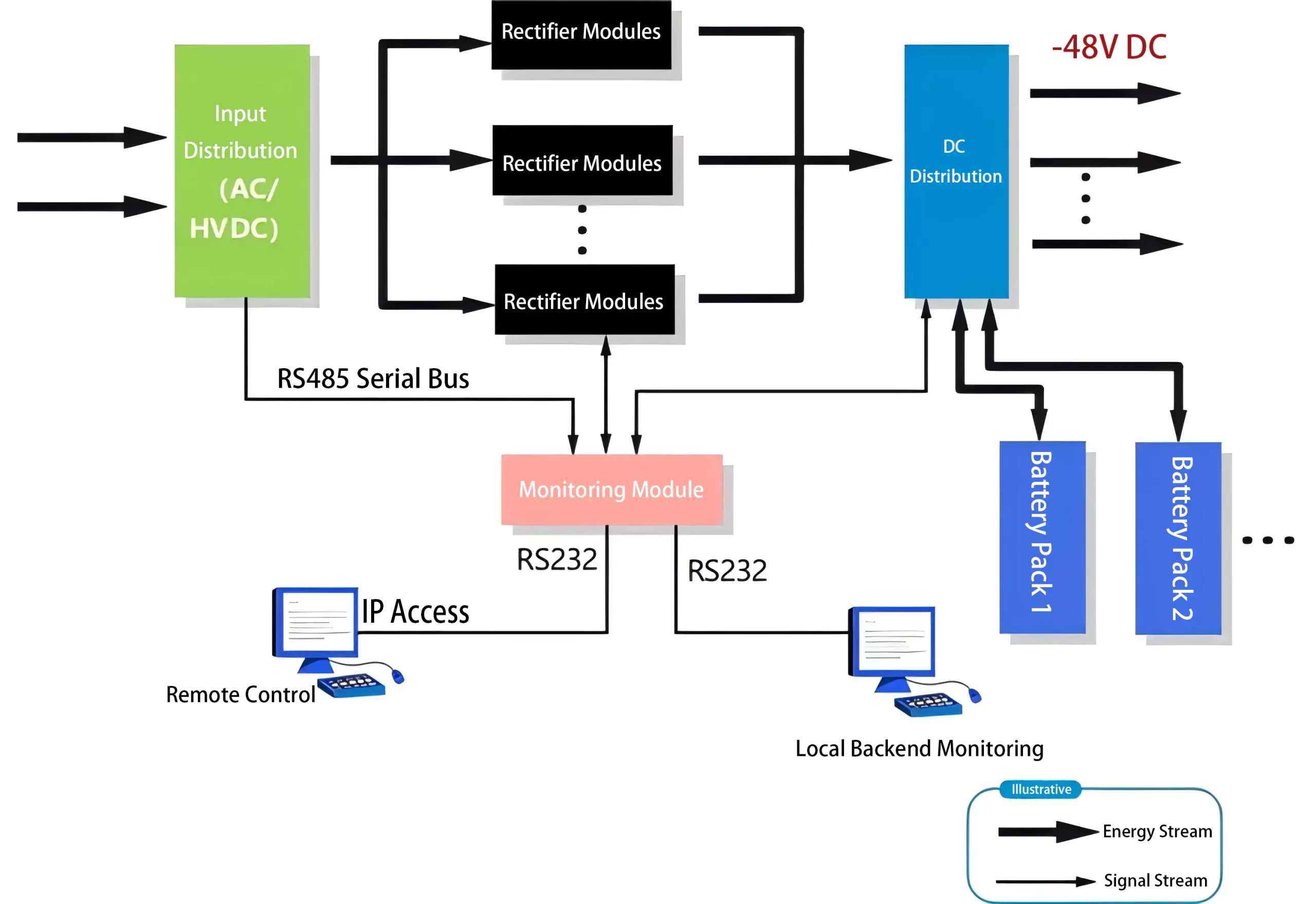
2024-12-26 MORE+

2024-12-26 MORE+

2024-12-26 MORE+
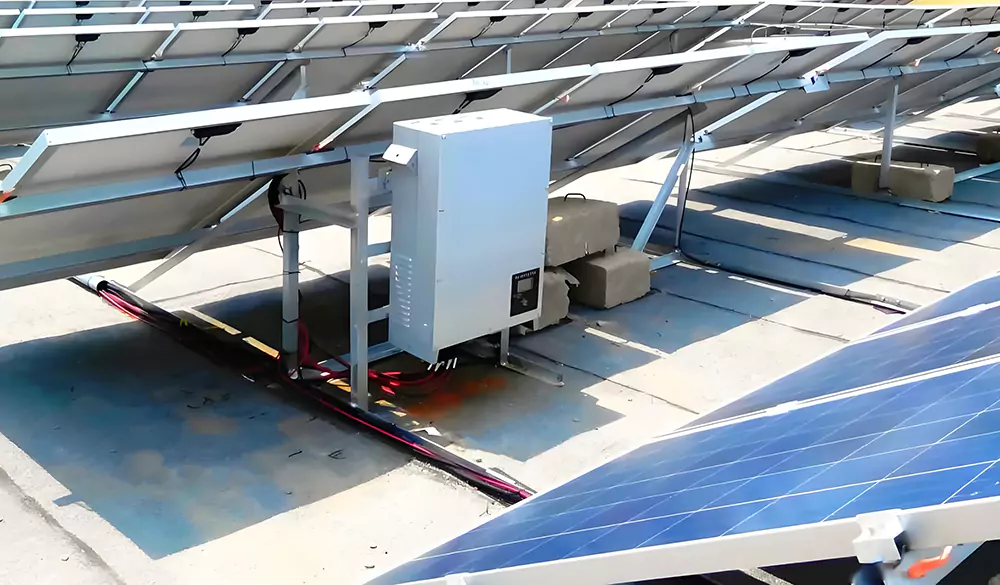

2024-12-26 MORE+
We're here to answer your questions and provide the energy solutions that best fit your needs.